Iran’s presidential election in 2024 is shaping up to be a three-way race
Stasis Consulting: The latest survey from Statis Consulting predicts the June 28 presidential election will be a close three-way race between two Principlist candidates, hardliner Saeed Jalili and moderate Principlist Mohammad Bagher Qalibaf, and one Reformist candidate, Masoud Pezeshkian.
This information is based on a representative poll conducted by Stasis Consulting between June 12-21, 2024, among 1,223 respondents.
An interactive visualization of the results of this poll can be found at the following link.
Iran’s presidential election in 2024 is shaping up to be a three-way race.
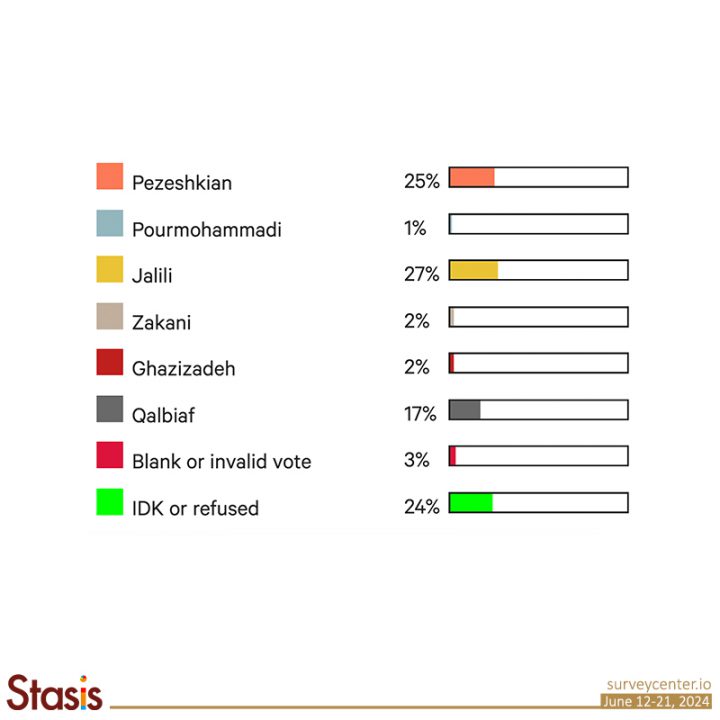
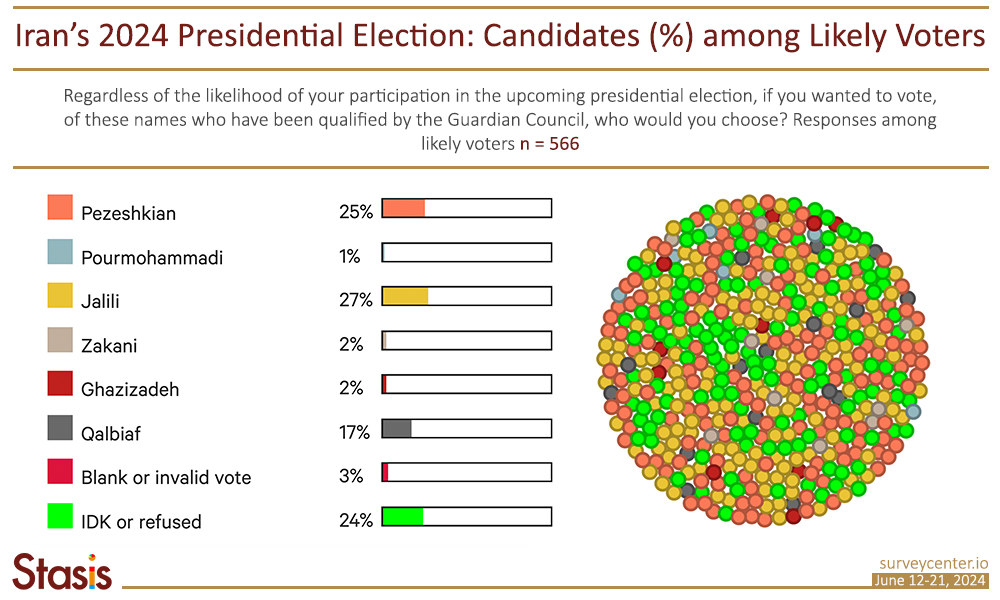
Iran’s presidential election in 2024 is shaping up to be a three-way race. Recent survey results indicate tight competition between the main candidates: hardliner Saeed Jalili, Reformist Masoud Pezeshkian, and moderate Principlist Mohammad Bagher Qalibaf. The poll shows that 27 percent of likely voters (n=566) support Jalili, followed by Pezeshkian at 25 percent, and Qalibaf at 17 percent.
Election Turnout
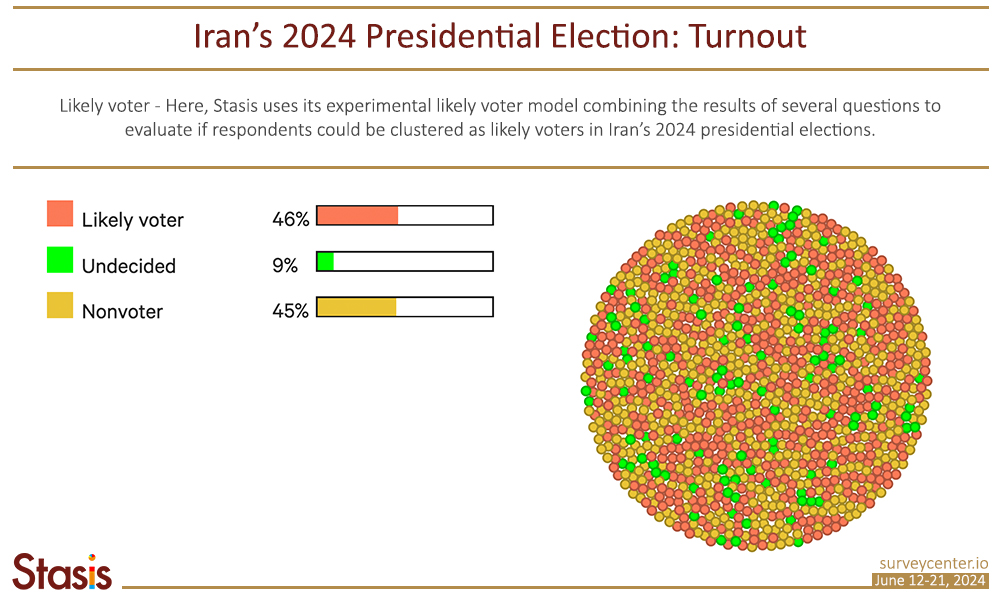
Stasis Consulting predicts a higher voter turnout than in previous elections, estimating at least 46% participation. Stasis uses a proprietary likely voter model, analyzing responses to different questions (defined in the methodology section) to identify probable voters. As of June 21, nine percent of the electorate is still undecided, while 45 percent do not plan to participate in the election.
Awareness of the election date among Iranians is higher than the previous Majlis Election
According to this survey, 51 percent of citizens know exactly when the presidential election will be held (June 28, 2024). This is a 23-percentage point improvement in crucial civic awareness among Iranians over the last parliamentary election, held four months ago. Moreover, Fifty-seven percent of respondents in this survey believe that the 2024 presidential election will be competitive, as opposed to 27 percent of interviewees who have a different view.
Remarks
The results of this poll have been interactively visualized in this link. This is an interactive platform detailing the results of every question, distinguished in a bar chart by gender, age group, location, and education.
For each question, there is also a bubble chart (consisting of many small circles), detailing the respondents’ information. Each circle represents a single respondent; clicking on any given circle will generate the complete answer set for that particular respondent. The color coding is consistent between the bubble chart and bar chart for easy comparison.
Stasis uses our proprietary likely voter model, analyzing responses to different questions to identify probable voters. Criteria for likely voters include a) knowing (exactly or approximately) the election date, b) saying that they are very likely to participate in the election, c) not saying “I don’t know” or refusing to answer the question about the likelihood of their participation in the election, and d) mentioning that their participation might depend on some factors.
Methodology
Survey methodology explained below:
- Telephone interviews were conducted between June 1221, 2024, among 1,223 respondents aged 18 and older living in Iran. Native Farsi speakers conducted the interviews during daytime hours.
- The proportional two-stage sample includes respondents from every province. Provinces have been sampled based on their population.
- Out of 1,223 respondents in unweighted data, 78% live in urban areas and 22% live in rural areas. Additionally, the sample consists of 58% male and 42% female respondents. Seventeen percent fall into the 18-29 age group, 73% in the 30-64 age group, and 10% in the 65 and up age group. All provinces except Tehran are represented in the sample by no more than ±2% of their population share. The province of Tehran is underrepresented by 5.1% in this unweighted sample.
- Results are weighted by gender, age, location (urban vs. rural areas), and adjusted for Tehran’s province based on the Iranian national census of 2016, the 2018 statistical yearbook, and Iran’s Statistical Center demographic predictions for the year 2024.
- Based on the sample, there is a 95 percent confidence that the margin of sampling error is within ±2.8 percentage points.
- Rates of respondent candor and reliability were appraised by experienced interviewers. Fifty-eight persons found to be lacking in these areas were removed from the sample and are not included in the final sample or in this report.
- The response rate for this survey was 32.3%.
- Stasis uses a proprietary likely voter model, analyzing responses to questions 13, 14, 16, and 26 to identify probable voters. Criteria for likely voters include a) those who express a likelihood of voting in question 14, b) do not respond with “I don’t know / Refused to answer” in question 13, and c) do not select vague options (it depends or made no decision yet) in questions 14, 16, and 26.